Ethereum, the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, has seen a significant decrease in its total supply for the first time since its launch in 2015. As of January 16th, 2023, Ethereum went deflationary, and its total supply has fallen by nearly 67,000 eth, equivalent to $122 million, at the time of writing. This article explores the reasons behind Ethereum’s supply drop and the impact of new entrants on the top burners leaderboard. Additionally, we will discuss the significance of these developments and their implications for the future of Ethereum.
Why has Ethereum’s supply decreased?
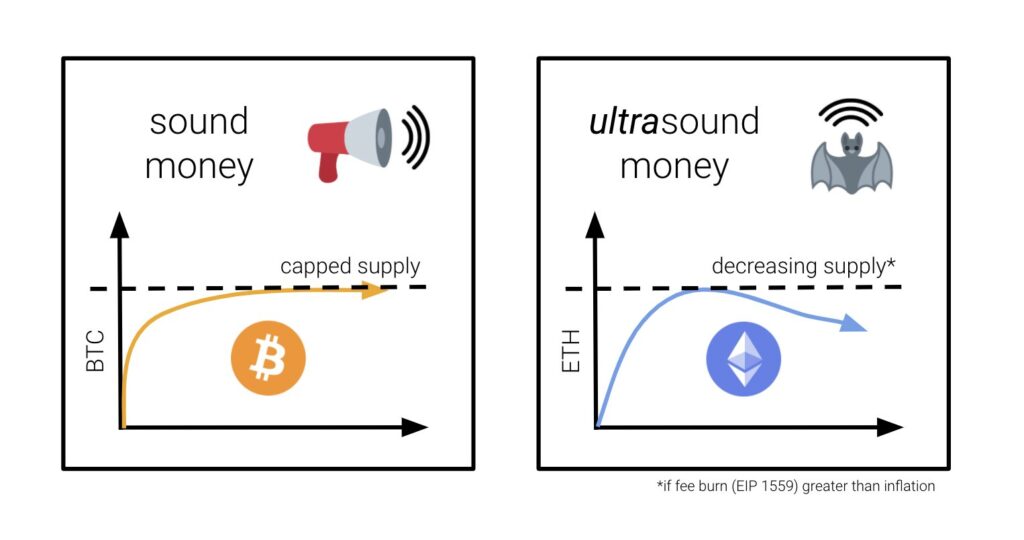
Ethereum’s supply drop can be attributed to its transition from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, known as Ethereum 2.0. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. In contrast, PoS requires validators to stake their coins to participate in the network’s consensus process, reducing energy consumption and improving scalability. As validators stake their Ethereum, they lock them up, effectively removing them from circulation. This process results in a decrease in the total supply of Ethereum, leading to deflation.
What is the impact of new entrants on the top burners leaderboard?
The top burners leaderboard tracks the top addresses that burn Ethereum coins through transactions. Two new entrants to the leaderboard, Arbitrum and zkSync, are second-layer solutions built on top of Ethereum. Arbitrum is one of the first second-layer solutions based on optimistic rollups to launch on Ethereum. It assumes off-chain transactions are valid, reducing congestion and transaction fees on the Ethereum network. The project is airdropping its Arb token to 600,000 addresses, which is expected to increase the usage of the platform.
Similarly, zkSync is a second-layer solution that uses zero-knowledge proofs (zk-proofs) to enable fast and cheap transactions. The project has not yet launched an airdrop but has opened its mainnet to developers, with a full zkEVM launch expected later this year. The entrance of these two projects into the burn leaderboard signifies a significant change in Ethereum’s landscape. These solutions are finding usage and may have a significant impact on the network’s capacity and scalability.
What does the future hold for Ethereum?
The future of Ethereum looks bright, with the entrance of second-layer solutions and the transition to Ethereum 2.0. The deflationary aspect of Ethereum may reduce the available supply, leading to price appreciation. The usage of these second-layer solutions may also lead to increased adoption of Ethereum, boosting its market capitalization.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed, such as regulatory concerns and competition from other blockchain platforms. Nonetheless, Ethereum’s transition to a more sustainable consensus algorithm and the development of second-layer solutions are significant steps towards addressing these challenges and ensuring the network’s growth and longevity.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s total supply has decreased significantly since its transition to Ethereum 2.0, with the entrance of second-layer solutions such as Arbitrum and zkSync playing a significant role. The usage of these solutions may increase the network’s capacity and scalability, leading to increased adoption and market capitalization. Despite challenges, Ethereum’s future looks promising, and investors should keep an eye on its developments.
The post Ethereum’s Total Supply Falls appeared first on YourCryptoLibrary.



